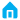
What is Industrial Robot Programming?
Industrial robot programming involves creating a set of instructions that enable a robot to perform specific tasks within a manufacturing environment. These tasks can range from simple pick - and - place operations to complex welding, painting, or assembly procedures. The programming process defines the robot's movements, speed, acceleration, and interaction with other equipment and materials.
Step - by - Step Guide to Industrial Robot Programming
Step 1: Define the Task
Clearly outline the task that the robot needs to perform. This includes determining the starting and ending positions, the path of movement, the speed and acceleration requirements, and any interaction with other objects or equipment. For example, if the robot is tasked with picking up a part from a conveyor belt and placing it in a specific location, you need to define the exact coordinates of these positions and the optimal speed for a smooth operation.
Step 2: Set Up the Workcell
Ensure that the robot's workcell is properly set up and calibrated. This involves installing the robot in its designated position, connecting all the necessary cables and sensors, and verifying that the end - effector (the tool attached to the robot's arm) is correctly mounted and functioning. Calibration is crucial to ensure accurate positioning and movement of the robot.
Step 3: Choose the Programming Method
Based on the complexity of the task and your level of expertise, select the most appropriate programming method. For simple tasks, teach - by - demonstration may be sufficient, while for more complex operations, off - line programming may be the better choice.
Step 4: Create the Program
-
Teach - by - Demonstration: Use the teach pendant to manually move the robot through the desired path, recording key positions at regular intervals. Once all the positions are recorded, the robot will generate a motion sequence based on these points.
-
Off - Line Programming: Open the OLP software and create a 3D model of the workcell, including the robot, the part to be manipulated, and any other relevant objects. Use the software's tools to define the robot's movements, speed, and acceleration. You can also simulate the program to check for collisions and optimize the path.
Step 5: Test and Debug the Program
Before deploying the program on the actual robot, thoroughly test it in a simulated environment (if using OLP) or in a safe, controlled setting. Check for any errors, such as incorrect positioning, collisions, or abnormal movements. Make necessary adjustments to the program to ensure smooth and accurate operation.
Step 6: Deploy and Optimize the Program
Once the program has been tested and debugged, deploy it on the actual robot. Monitor the robot's performance during production and make further optimizations as needed. This may involve adjusting the speed, acceleration, or path of movement to improve efficiency and quality.

 Il tuo messaggio deve contenere da 20 a 3000 caratteri!
Il tuo messaggio deve contenere da 20 a 3000 caratteri! Si prega di controllare la tua email!
Si prega di controllare la tua email!  Il tuo messaggio deve contenere da 20 a 3000 caratteri!
Il tuo messaggio deve contenere da 20 a 3000 caratteri! Si prega di controllare la tua email!
Si prega di controllare la tua email!